13 January 2023
Market integration of electric vehicles using blockchain technology
Electric vehicles (EV) are the fastest growing decentralized energy resources (DER).
Why this project
They will not only constitute a large share of the future energy demand but also provide a source of decentralized flexibility for our ancillary services, i.e., to support the grid stability or prevent congestions.
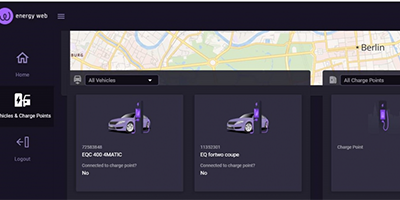
To enable a scalable market access for EVs, there is a need for proper asset identification. This is especially true for non-stationary EVs connected to different charging poles (CP).
To address this issue, we built a decentralized registry to test the authentication and authorization of electric vehicles and charging poles for the balancing market. With the help of decentralized identifier (DID), we can now demonstrate a new way of asset identification for an easier market access.
Approach
The power system is one of the most critical infrastructures of our country and participation in that system requires high security standards. Today this is ensured by a complex pre-qualification process where technical capabilities, ownership information and communication requirements are verified. Compared to stationary assets, the integration of electric vehicle brings new challenges: Countless types of car models, complex ownership structures, changing grid connection points as well as various services providers that want to interact with the device are just few examples. Integrating EVs into the network will require a new way of identification and interaction.
In the first proof of concept of the DLT Lab (see box on the right), we developed a registry for electric vehicles and charging stations using software development toolkits from Energy Web Foundation. The registry demonstrates a new way of onboarding small flexibility sources to the balancing market using decentralized identifiers (DID). DIDs are like digital passports anchored on a blockchain. They allow the verification of claims from actors of the decentralized network. These claims can contain asset data, ownership relations or any other relevant information. Blockchain technology ensures that the information cannot be changed unilaterally, this means data cannot be tampered.
We use the concept of DID to authenticate the identity and attributes of electric vehicles to authorize their participation in the balancing market.
Results
-
We build on open-source solutionsThe architecture of the current PoC starts with a node on the Open Charging Network (OCN), an open source e-mobility roaming platform, which serves as an interface to the e-mobility ecosystem. Mobility Service Providers and Charging Point Operators can easily connect to the OCN and hence with the registry.
-
Full decentraliziation in a public blockchainWe want an open and non-discriminatory interaction to enable the full potential of decentralized technologies, which is why we chose a public blockchain. A user interface allows the selection of different market roles such as TSO, DSO, CPO, MSP and aggregators.
-
How we use verifiable credentialsThe first process demonstrates an authorization process for vehicles and charging stations. The MSP or CPO are able to request an authorization to participate in the balancing market. We, the TSO, get notified upon that request and are able to read technical information from the DID document. Finally, this allows us approve participation in form of a verifiable credential on the DID document of the asset or for all types of the same asset.
-
We invite everyone to join our developmentCurrently we are working in simulation mode but are already busy with the integration of real devices. If this is of interest for you, we invite you to contact us to assess the potential of a collaboration.